Art, Design and Technology




Our KS3 curriculum at Alderman White in Art, Design and Technology delivers learning that gives young people a varied breadth and depth of subject knowledge, core skills and a strong technical understanding which aids their personal development and provides every child with the opportunity to achieve whilst gaining life-long learning experiences. We aim for students to acquire knowledge that gives them a strong understanding of the world around them. Students will not only obtain knowledge, but will also develop understanding whilst practicing home skills that make them able to contribute and add value to our community at a local, national and global level. The Art, Design and Technology curriculum at Alderman White are stimulating, rigorous and practical subjects encompassing the specialist areas of Art and Design, Product Design, Graphics, Food, and Textiles.
Our curriculum strives to inspire, motivate and present a range of opportunities for students to develop their creative, practical and technical skills. Students design and make prototypes and products that solve real life problems within a variety of contexts, considering both their own and others’ needs, wants and values.
Everything around us has been designed, the clothes that we wear, the technology that we use, the buildings that we occupy, the food that we eat, the media that we view. Art, Design and Technology at Alderman White allows students to be inspired to learn and want to do more. It gives them opportunities that are both challenging and aid personal development for lifelong learning. Art, Design and Technology is a way of doing things logically, it is a way of thinking creatively and applying what students learn for their future pathways to their careers and professions. We encourage students to take risks, within a safe environment, to design and create innovative solutions to real life problems. We aim to foster a generation of creative thinkers, designers and practitioners. Art, Design and Technology allows curiosity, inspiration, imagination and motivation, leading to further study and careers in a range of sectors.
Through the subjects of Art, Design and Technology our aim is for all students to embrace and enjoy the subject matter across all disciplines in KS3. As students build and develop their skills, knowledge and understanding, this ultimately supports them in their future preparation choices in regards to Year 9 options.
Key Stage 3
By the end of KS3 (years 7,8,9) our Design and Technology students should:
Design
- use research and exploration, such as the study of different cultures, to identify and understand user needs.
- identify and solve their own design problems and understand how to reformulate problems given to them.
- develop specifications to inform the design of innovative, functional, appealing products that respond to needs in a variety of situations.
- use a variety of approaches [for example, biomimicry and user-centred design] to generate creative ideas and avoid stereotypical responses.
- develop and communicate design ideas using annotated sketches, detailed plans, 3-D and mathematical modelling, oral and digital presentations.
Make
- select from and use specialist tools, techniques, processes, equipment and machinery precisely, including computer-aided manufacture.
- select from and use a wider, more complex range of materials, components and ingredients, considering their properties.
Evaluate
- analyse the work of past and present professionals and others to develop and broaden their understanding
- investigate new and emerging technologies
- test, evaluate and refine their ideas and products against a specification, considering the views of intended users and other interested groups
- understand developments in design and technology, its impact on individuals, society and the environment, and the responsibilities of designers, engineers and technologists
Technical knowledge
- understand and use the properties of materials and the performance of structural elements to achieve functioning solutions
- understand how more advanced mechanical systems used in their products enable changes in movement and force
- understand how more advanced electrical and electronic systems can be powered and used in their products [for example, circuits with heat, light, sound and movement as inputs and outputs]
- apply computing and use electronics to embed intelligence in products that respond to inputs [for example, sensors] and control outputs [for example, actuators] using programmable components [for example, microcontrollers]
Cooking and Nutrition
- understand and apply the principles of nutrition and health
- cook a repertoire of predominantly savoury dishes so that they are able to feed themselves and others a healthy and varied diet
- become competent in a range of cooking techniques [for example, selecting and preparing ingredients; using utensils and electrical equipment; applying heat in different ways; using awareness of taste, texture and smell to decide how to season dishes and combine ingredients; adapting and using their own recipes]
- understand the source, seasonality and characteristics of a broad range of ingredients
By the end of KS3 (years 7,8,9) our Art students should:
- to use a range of techniques to record their observations in sketchbooks, journals and other media as a basis for exploring their ideas
- to use a range of techniques and media, including paintingto increase their proficiency in the handling of different materials
- to analyse and evaluate their own work, and that of others, in order to strengthen the visual impact or applications of their work
- about the history of art, craft, design and architecture, including periods, styles and major movements from ancient times up to the present day.
Key Stage 4
At KS4 students are given the opportunity to focus on their chosen specialism and opt for the course that best suits their own career aspirations or interests. At Alderman White we currently offer the following ks4 options: Art, Food Preparation and Nutrition, Textiles and GCSE Design and Technology.
By the end of KS4 (years 10 and 11) students who choose to study Art should:
Knowledge, understanding and skills
Students must develop and apply the knowledge, understanding and skills specified in the Subject content within the context of fine art practice and their selected area(s) of study.
The following aspects of the knowledge, understanding and skills are defined in further detail to ensure students’ work is clearly focused and relevant to fine art.
Knowledge and understanding
The way sources inspire the development of ideas, relevant to fine art including:
- how sources relate to individual, social, historical, environmental, cultural, ethical and/or issues-based contexts
- how ideas, themes, forms, feelings and concerns can inspire personally determined responses that are primarily aesthetic, intellectual or conceptual.
- The ways in which meanings, ideas and intentions relevant to fine art can be communicated including the use of:
figurative representation, abstraction, stylisation, simplification, expression, exaggeration and imaginative interpretation visual and tactile elements, such as:
- colour
- line
- form
- tone
- texture
- shape
- composition
- rhythm
- scale
- structure
- Skills
Within the context of fine art, students must demonstrate the ability to:
- use fine art techniques and processes, appropriate to students’ personal intentions, for example:
- mark-making
- monoprint, collagraph and block printing
- assemblage
- construction
- carving
- film and video
- digital working methods
- use media and materials, as appropriate to students’ personal intentions, for example:
- charcoal, pastels, pen and ink, crayons and pencil
- watercolour, gouache, acrylic and oil paint
- found materials
- clay, wood and metal
- digital imagery
- different papers and surfaces on which to work.
![]() Exam Board Specification | Fine Art
Exam Board Specification | Fine Art
By the end of KS4 (years 10 and 11) students who choose to study Food Preparation and nutrition should:
- be able to demonstrate effective and safe cooking skills by planning, preparing and cooking a variety of food commodities whilst using different cooking techniques and equipment
- develop knowledge and understanding of the functional properties and chemical characteristics of food as well as a sound knowledge of the nutritional content of food and drinks
- understand the relationship between diet, nutrition and health, including the physiological and psychological effects of poor diet and health
- understand the economic, environmental, ethical and socio-cultural influences on food availability, production processes, diet and health choices
- demonstrate knowledge and understanding of functional and nutritional properties, sensory qualities and microbiological food safety considerations when preparing, processing, storing, cooking and serving food
- understand and explore a range of ingredients and processes from different culinary traditions (traditional British and international) to inspire new ideas or modify existing recipes.
![]() Exam Board Specification | GCSE Food Preparation and Nutrition
Exam Board Specification | GCSE Food Preparation and Nutrition
GCSE Design and Technology (Textiles and Product Design)
GCSE Design and Technology (Textiles or Resistant Materials route)
The GCSE in Design and Technology enables students to understand and apply iterative design processes through which they explore, create and evaluate a range of outcomes. The qualification enables students to use creativity and imagination to design and make prototypes (together with evidence of modelling to develop and prove product concept and function) that solve real and relevant problems, considering their own and others’ needs, wants and values. It gives students opportunities to apply knowledge from other disciplines, including mathematics, science, art and design, computing and the humanities.
During the NEA Students can choose to make products from a range of materials including Textiles, Timbers and Metal, Polymers and Paper and Card.
The written paper is one paper.
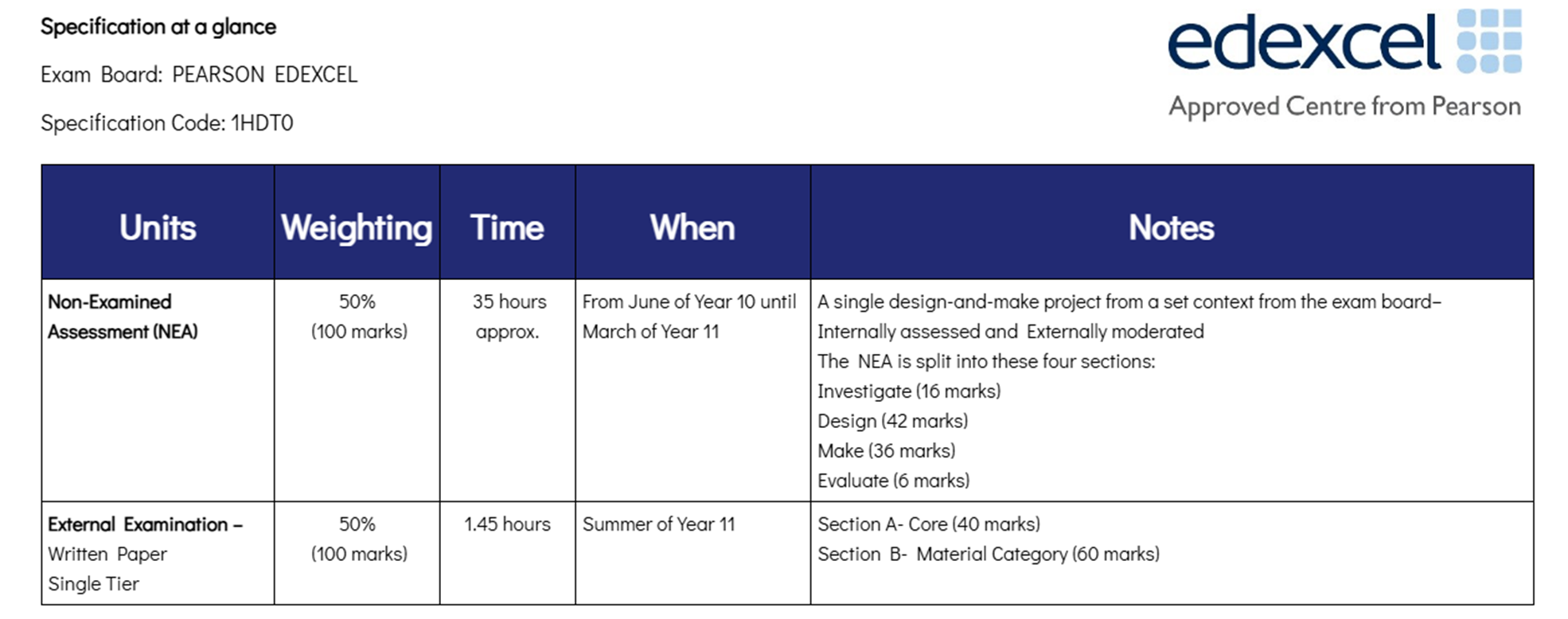
Course Content:
The GCSE Design and Technology course emphasizes the application of iterative design processes, enabling students to explore, create, and evaluate a range of design outcomes. Students will develop their creativity and imagination to produce prototypes that address real and relevant problems, considering diverse needs and values.
Classroom Activities:
Lessons will involve focused practical tasks to cultivate personal skills and knowledge, culminating in the design and manufacture of a major practical project. Theoretical written work will be integrated to support practical and design concepts.
Homework Expectations:
Homework will extend classroom learning and provide essential support for the organization of practical work and the NEA task. It is also crucial for examination preparation and revision. Ongoing Assessment and Feedback: Regular dialogue and feedback will be provided to inform students of their current attainment and targets for improvement.
Differentiation Strategies:
GCSE Design and Technology is taught in mixed-ability groups. In Year 10, all students will engage in the same mini-project work, with support and extension opportunities available. The NEA and final written examination are standardized by Edexcel, with performance criteria aligned to grades 9-1.

